 6, Prem Kutir, Universtiy Road, Udaipur – 313001 Rajasthan, India
6, Prem Kutir, Universtiy Road, Udaipur – 313001 Rajasthan, India [email protected]
[email protected] 09414234600, 7737447183
09414234600, 7737447183
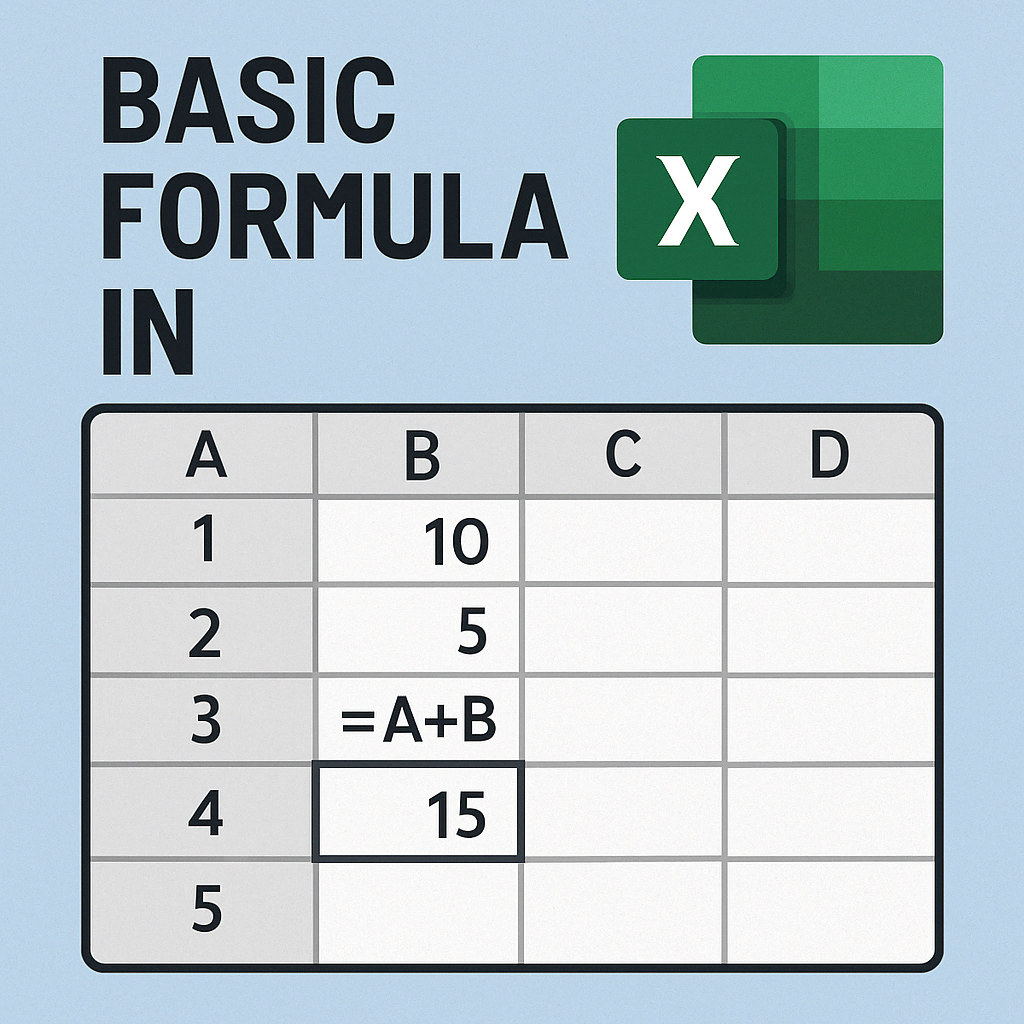
Formula
Microsoft Excel is a powerful tool for managing data and performing calculations. With the help of formulas, we can perform simple as well as complex tasks easily.
In this blog by Anil Computers, Udaipur, we will learn 24 most important Excel formulas with explanation, syntax, and examples.
Purpose: Adds two or more numbers together.
Syntax:
Example:=SUM(10,20,30) → Result: 60=SUM(A1:A5) → Adds all numbers in cells A1 to A5.
Purpose: Finds the average (mean) of given numbers.
Syntax:
Example:=AVERAGE(10,20,30) → Result: 20=AVERAGE(A1:A5) → Finds average of values in A1 to A5.
Purpose: Finds the largest number from a list of values.
Syntax:
Example:=MAX(10,50,30) → Result: 50
Purpose: Finds the smallest number from a list of values.
Syntax:
Example:=MIN(10,50,30) → Result: 10
Purpose: Counts the total number of characters (letters, numbers, spaces, symbols) in a cell.
Syntax:
Example:=LEN("Excel") → Result: 5=LEN("Excel 2025") → Result: 10
Purpose: Converts text into UPPERCASE letters.
Syntax:
Example:=UPPER("excel") → Result: EXCEL
Purpose: Converts text into lowercase letters.
Syntax:
Example:=LOWER("EXCEL") → Result: excel
Purpose: Multiplies numbers.
Syntax:
Example:=PRODUCT(5,4,3) → Result: 60
Purpose: Counts only numbers in selected cells.
Syntax:
Example:=COUNT(10,"Excel",20) → Result: 2 (counts only numbers)
Purpose: Counts all non-empty cells (numbers + text).
Syntax:
Example:=COUNTA(10,"Excel",20) → Result: 3
Purpose: Returns the factorial of a number.
Syntax:
Example:=FACT(5) → Result: 120 (5×4×3×2×1)
Purpose: Returns power of a number.
Syntax:
Example:=POWER(2,3) → Result: 8
Purpose: Returns the square root of a number.
Syntax:
Example:=SQRT(25) → Result: 5
Purpose: Capitalizes the first letter of each word.
Syntax:
Example:=PROPER("excel formula") → Result: Excel Formula
Purpose: Displays current date.
Syntax:
Example:
If today is 2 Sept 2025 → Result: 02-09-2025
Purpose: Displays current date and time.
Syntax:
Example:
Result: 02-09-2025 11:35 AM
Purpose: Rounds a number to specific decimal places.
Syntax:
Example:=ROUND(12.345,2) → Result: 12.35
Purpose: Rounds a number up to the nearest even number.
Syntax:
Example:=EVEN(13) → Result: 14
Purpose: Rounds a number up to the nearest odd number.
Syntax:
Example:=ODD(14) → Result: 15
Purpose: Returns the remainder after division.
Syntax:
Example:=MOD(10,3) → Result: 1
Purpose: Returns only the integer part of a division.
Syntax:
Example:=QUOTIENT(20,6) → Result: 3
Purpose: Counts cells that meet a specific condition.
Syntax:
Example:=COUNTIF(A1:A5,">10") → Counts values greater than 10.
Purpose: Calculates discount on price.
Formula:
Example:
If price = 1000 and discount = 10%=1000*10% → Result: 100
Purpose: Finds percentage of a number.
Formula:
Example:=(50/200)*100 → Result: 25%
These 24 Excel formulas are the building blocks for anyone who wants to master Excel. They are useful for students, accountants, office staff, and business professionals.
At Anil Computers, Udaipur, we provide Excel, Tally, Marg ERP, Photoshop, and Digital Marketing training with practical examples.
Master Basic Excel Formulas: SUM, AVERAGE & More in Hindi
Thanks TO Google
Thanks To ChatGpt